Today (January 9, 1922) is the birthday of Nobel laureate Har Gobind Khorana, who researched the genetic code and its role in the synthetic production of protein.

Har Gobind Khorana was born on January 9, 1922, in the village of
Raipur, Punjab, the fifth child. His father worked as a tax collector in the
village. Although his family grew up in poverty, his father was keen on
educating his children. In his village of about 100 families, only the family
of Khorana was literate. Khorana's primary education began at a village school
under a tree. From an early age, he excelled in his studies. He attended DAV
High School in Multan, West Bengal. He was fascinated by the author
'Rathanlal'. He completed his schooling and continued his studies at Punjab
University, Lahore. Passed first class in B.Sc degree. He completed his
postgraduate degree in Chemistry in 1945 under the supervision of Madan Singh,
a professor and eminent researcher here.

Khorana received a scholarship from the Government of India in 1945 to
study at the University of Liverpool in the United Kingdom and receive a
doctorate. Here 'Roger JS Peer' acted as his guide. After coming here he
started following the western cultural way. In 1948-49 he continued his
research at the Federal Institute of Technology in Switzerland. Professor
Vladimir Brylak also guided his progress by developing a scientific interest,
involvement in the work, and the development of corresponding skills. Khorana
went to Canada in 1952, where he befriended Esther Elizabeth Sipler, the
daughter of a Swiss parliamentarian. Then she married him. The couple had two
daughters and a son. At the end of 1949, India returned to India. After months
of unemployment in India, Khorana returned to the UK with the intention of
further research.

Dr GW Kenner co-authored the study with Nobel Prize-winning scientist
Sir Alexander Todd. Involved in the study of proteins and nucleic acids in
1950-52. In 1952 he became a researcher at the British Columbia Laboratory at
the invitation of Dr Gordon M. Shrum. Despite Dr Shram's encouragement, Dr
Jack Kemble undertook research on phosphate esters and nucleic acids. Although
many others with him contributed to the study, 'Dr. Gordon M. Tener 'was a
great guide to the team's research progress. In 1960 he joined the Institute
for the Study of Enzymes at the University of Wisconsin and continued all research.
He was then granted citizenship in the United States. From 1962 to 1970 he was
a professor, professor of biochemistry and deputy director of the institute.

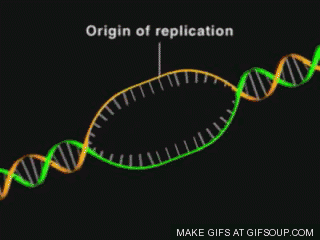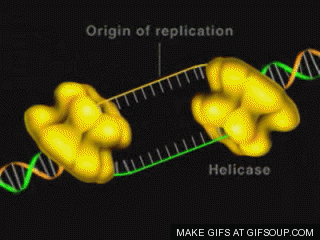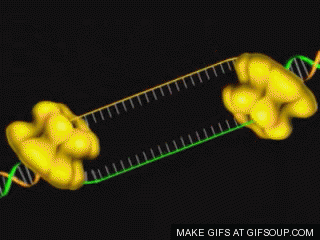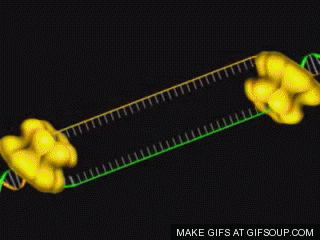
In 1959, Khorana developed a chemical called coenzyme-A, which is
essential for certain processes in the human body. The following year, Curana
travelled to the United States to work with his Nobel Prize-winning fellow
researcher, Marshall Norenberg, at the University of Wisconsin Enzyme Research
Institute. There they discovered that some of the inherited diseases could be
cured as a result of their research. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
was awarded in 1968 to Khorana, Norenberg and Holley for their research on
genetic code and their role in the synthetic production of protein. Khorana was
later awarded the title of Professor of Biology and Chemistry at the
Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1970. There, his work on the genetic
code became world-famous. Scientists at the University of Cambridge have
already studied the structure of Escherichia coli bacteria in the gut of humans
and animals.


Khorana and his team were involved in the genetic development of the
microbe. Gradually, they synthesized about 207 genes of the bacterium. Then in
August 1976, the synthetic gene was inserted into the Escherichia coli
bacterium, which acted similarly to the natural gene. The world marvelled at
this achievement. It took Khorana and the 24 assistants on his team about nine
years to successfully complete their studies. Even with the Nobel Prize, Corona
has won many more prizes and awards. In 1969 he was awarded the Padma Bhushan.
In 1968, he was awarded the 'Distinguished Service Award' by the Wattumul
organization based in Honolulu, Hawaii. In 1971 it was awarded the American
Academy of Achievement Award by the American Academy of Philadelphia in
Pennsylvania. In 1972, the Bose Company 'J.C. Presented Bose 'medal.
He was awarded the Willard Gibbs Medal by the Chicago Division of
American Chemistry for 1973-74. Corona has received awards such as the 'Kirchner
Organization International Award', the 'Louisa Cross Horwitz Prize', and the
'Albert Lasker Prize for Basic Medical Research. He has been recognized as a
Fellow of the American National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of
Sciences. In 1971 he was accepted as a foreign member of the Russian Academy of
Sciences. In 1974 he was appointed an Honorary Research Fellow of the Indian
Chemical Society. He was appointed a member of the scientific governing board
of the Scripps Research Institute.


Madison, Wisconsin, High Technology, and the Indo-US Science and
Technology Organization co-founded the Khorana Program in 2007. It was created
in the name of Corona to continue research. It is attended by many scientists,
businessmen and social activists from India and the United States. Work is
ongoing to improve the research mindset of graduate, postgraduate and
postgraduate students, with an emphasis on rural development, food security,
etc. In 2009, Corona was invited to the event and was honoured. Har Gobind Khorana, the winner of the Nobel Prize for his
research into the synthetic production of protein, passed away on November 9,
2011, in Concord, Massachusetts, USA, at the age of 89.
Source By: Wikipedia
Information: Dr. P. Ramesh, Assistant Professor of Physics, Nehru Memorial College, Puthanampatti, Trichy.
Get information like this
https://t.me/joinchat/jpqj3jQLN51kYTk9
Join Telegram Group.
https://chat.whatsapp.com/FisIzCe4Br2CRgxAiicUnf
Join WhatsApp Group
Thanks.
Also, Read
🛑👍 CSIR-NET Physics Materials and Problems
🛑📕 21 GB and Hundreds of Physics E-Books Collection.
🛑🛥️ How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor).
🛑🤹♂️ Science Academies' Summer Research Fellowship Programme for Students and Teachers 2022.
🛑🔌 How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering.
🛑🎙️ Transistors Explained - How transistors work.
🛑🔥⚡ How Thermocouples Work - basic working principle.
🛑🔌 Voltage Explained - What is Voltage? Basic electricity potential difference
🛑🔌 What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics.
.jpeg)
.png)
.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment