Today (February 19, 1941) is the birthday of David Jonathan Gross, winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of quantum chromodynamics.


David Jonathan Gross was born on February 19, 1941, in Washington, DC,
USA to a Jewish family. His parents were Nora (Faine) and Bertram Myron Gross.
Gross received his bachelor's degree and master's degree from the Hebrew
University of Jerusalem, Israel, in 1962. He received his PhD in physics from
the University of California, Berkeley, in 1966, under the supervision of
Geoffrey Chew. He was a Junior Fellow at Harvard University and a Eugene
Higgins Professor of Physics at Princeton University until 1997 when he began
serving as Princeton's Thomas Jones Professor of Mathematical Physics Emeritus.
He has received many honours, including a MacArthur Foundation Fellowship in
1987, the Dirac Medal in 1988 and the Harvey Prize in 2000.


He has been a central figure in particle physics and string theory. In
1973, Professor Gross, working with his first graduate student, Frank Wilczek,
at Princeton University, discovered asymptotic freedom—the primary feature of
non-Abelian gauge theories—led Gross and Wilczek to the formulation of quantum
chromodynamics, the theory of the strong nuclear force. Asymptotic freedom is a
phenomenon where the nuclear force weakens at short distances, which explains
why experiments at very high energy can be understood as if nuclear particles
are made of non-interacting quarks. The flip side of asymptotic freedom is that
the force between quarks grows stronger as one tries to separate them.
Therefore, the closer quarks are to each other, the less the strong interaction
(or colour charge) is between them; when quarks are in extreme proximity, the
nuclear force between them is so weak that they behave almost as free
particles. This is the reason why the nucleus of an atom can never be broken
into its quark constituents.


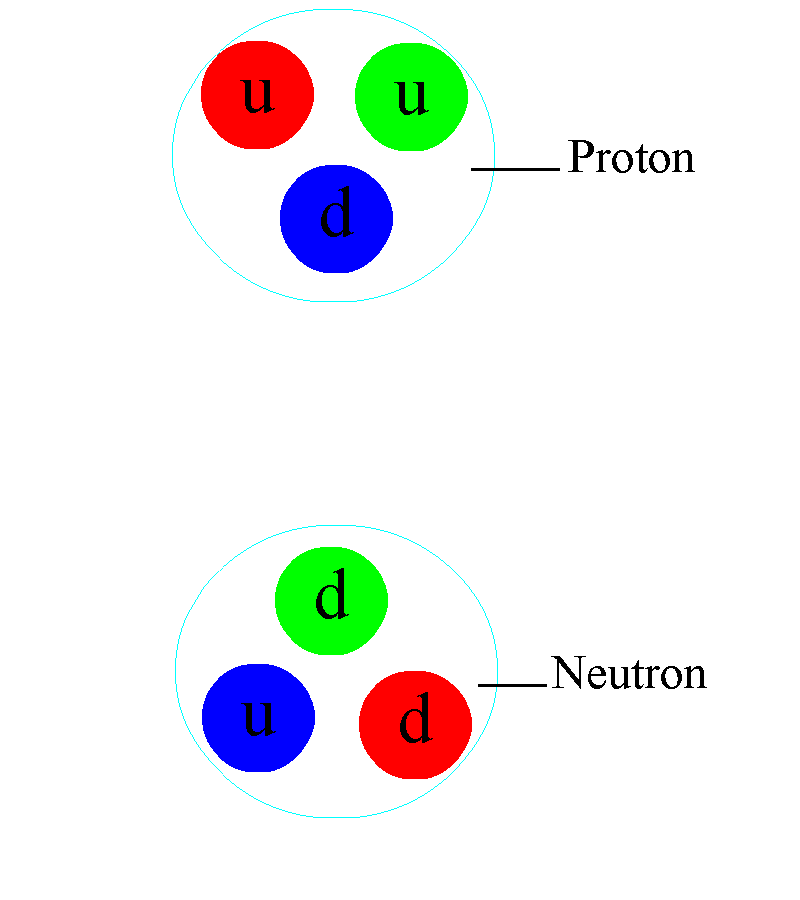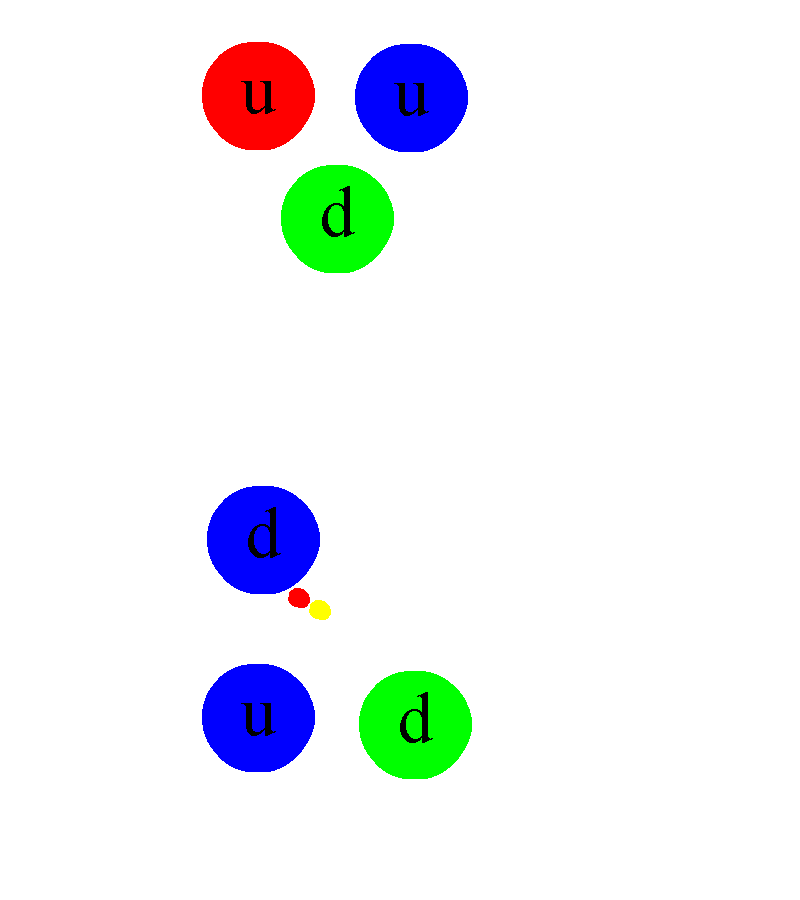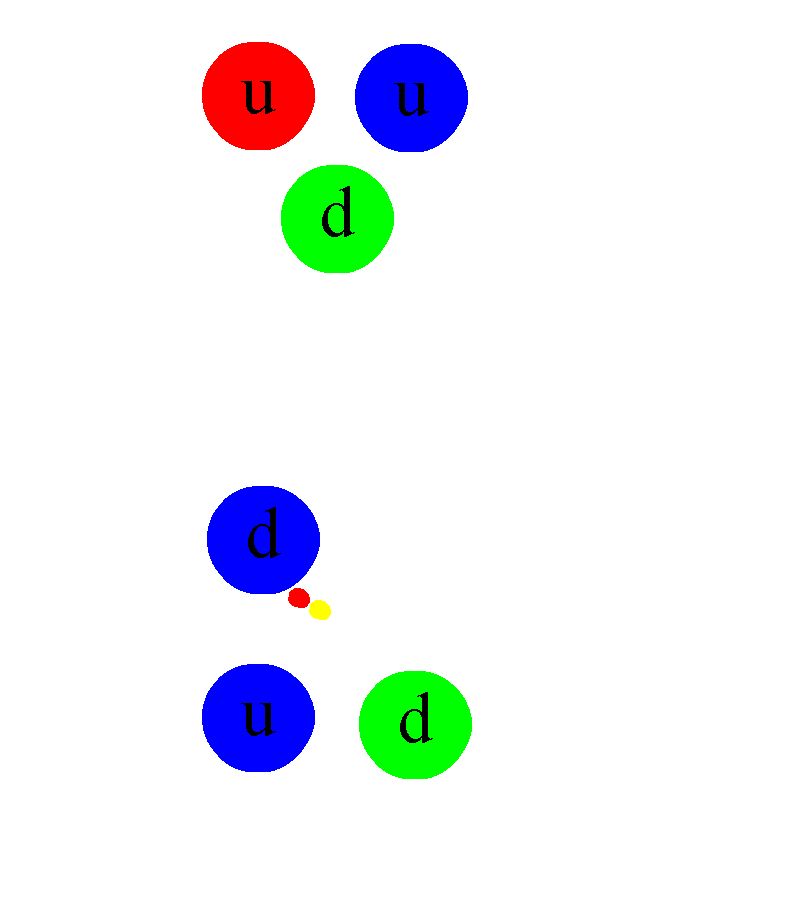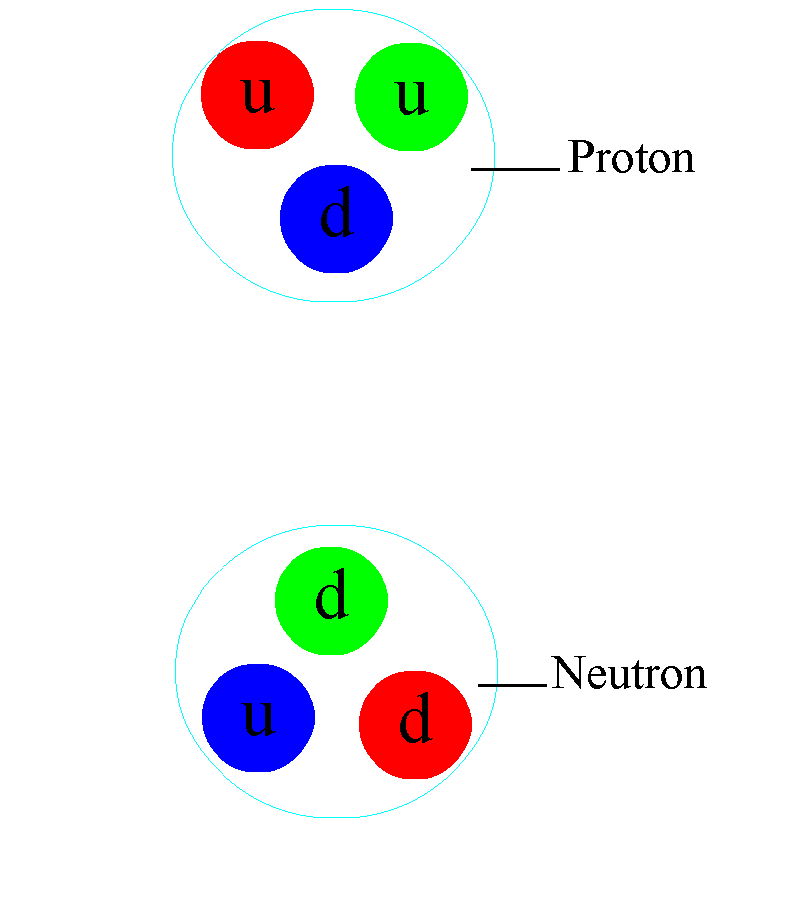
QCD completed the Standard Model, which details the three basic forces
of particle physics—the electromagnetic force, the weak force, and the strong
force. Gross was awarded the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physics, with Politzer and
Wilczek, for this discovery. Gross, with Jeffrey A. Harvey, Emil Martinec, and
Ryan Rohm also formulated the theory of the heterotic string. The four were
whimsically nicknamed the "Princeton String Quartet."He continues to
do research in this field at the KITP. In 2003, Gross was one of 22 Nobel
Laureates who signed the Humanist Manifesto, however, Gross is not an atheist. Gross
is one of the 20 American recipients of the Nobel Prize in Physics to sign a
letter addressed to President George W. Bush in May 2008, urging him to
"reverse the damage done to basic science research in the Fiscal Year 2008
Omnibus Appropriations Bill" by requesting additional emergency funding
for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, the National Science
Foundation, and the National Institute of Standards and Technology.

In 2015, Gross signed the Mainau Declaration 2015 on Climate Change on
the final day of the 65th Lindau Nobel Laureate Meeting. The declaration was
signed by a total of 76 Nobel Laureates and handed to then-President of the
French Republic, François Hollande, as part of the successful COP21 climate
summit in Paris.
Source By: Wikipedia
Information: Dr. P. Ramesh, Assistant Professor of Physics, Nehru Memorial
College, Puthanampatti, Trichy.
Get information like this
https://t.me/joinchat/jpqj3jQLN51kYTk9
Join Telegram Group.
https://chat.whatsapp.com/FisIzCe4Br2CRgxAiicUnf
Join WhatsApp Group
Thanks.
Also, Read
🛑👍 CSIR-NET Physics Materials and Problems
🛑📕 21 GB and Hundreds of Physics E-Books Collection.
🛑🛥️ How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor).
🛑🤹♂️ Science Academies' Summer Research Fellowship Programme for Students and Teachers 2022.
🛑🔌 How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering.
🛑🎙️ Transistors Explained - How transistors work.
🛑🔥⚡ How Thermocouples Work - basic working principle.
🛑🔌 Voltage Explained - What is Voltage? Basic electricity potential difference
🛑🔌 What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics.
.jpeg)
.png)
.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment