Today (February 1, 1905) is the birthday of Emilio Gino Segre, winner of the Nobel Prize for his discovery of the anti-proton.

Emilio Gino Segre was born on February 1, 1905, into a Separate Jewish
family in Tivoli, near Rome. He was the son of businessman Giuseppe Centre and
Amelia Susanna Treves, who owned a paper mill. He had two older brothers,
Angelo and Marco. He was educated at Ginnacio in DeVoli. After the family moved
to Rome in 1917, he graduated from Rome in July 1922 with the degree of Ginzio
and Also. Joined the University of Rome La Sabina as an engineering student.
In 1927, Segre met Franco Rosetti. Introduced him to Enrico Fermi. Two young
physics professors were looking for talented students.


In September 1927 they attended the Volta Conference in Como. There he
listened to Segre lectures from notable physicists, including Niels Born, Werner
Heisenberg, Robert Milligan, Wolfgang Bowley, Max Blank and Ernest Rutherford. Sergey
later joined Fermi and Rosetti in a laboratory in Rome. With the help of the
director of the Institute of Physics, Orzo Mario Corbino, Segre was able to
convert to physics, and, studying under Fermi, received his Laria degree in July
1928 in scattering and magnetic rotation. After serving in the Italian Army
from 1928 to 1929, he was appointed second lieutenant in antiaircraft artillery.

Segre published his first article on the irregular scattering of mercury
and lithium. In the 1930s, Zeke began to study the Zeeman effect on certain
alkaline metals. When his progress stalled because the diffraction criteria he
was to pursue were not available in Italy, he wrote a letter asking for help to
four laboratories elsewhere in Europe. Peter also received a call from Zeeman
to complete his work at Zeeman's laboratory in Amsterdam. Sacramento was
awarded the Rockefeller Foundation Fellowship. And on Fermi's advice, he was
selected to use it to study under Otto Stern in Hamburg. Working with Otto
Frisch in space measurement produced results that did not agree with the
current theory. But Isidore Isaac Rabbi showed that theory and experiment agree
if the nuclear vortex of potassium is +1/2.


From 1943 to 1946 he served as team leader for the Manhattan Project at
the Los Alamos National Laboratory. In April 1944 he discovered that the
proposed plutonium gun-type nuclear weapon Thin Man would not work because of
the presence of plutonium-240 contaminants. Returning to Berkeley in 1946, he became
Professor of Physics and Scientific History, working until 1972. Seckray and
Owen Chamberlain were co-chairs of a research team at the Lawrence Radiation
Laboratory. On December 11, 1959, Owen shared the Nobel Prize with Chamberlain
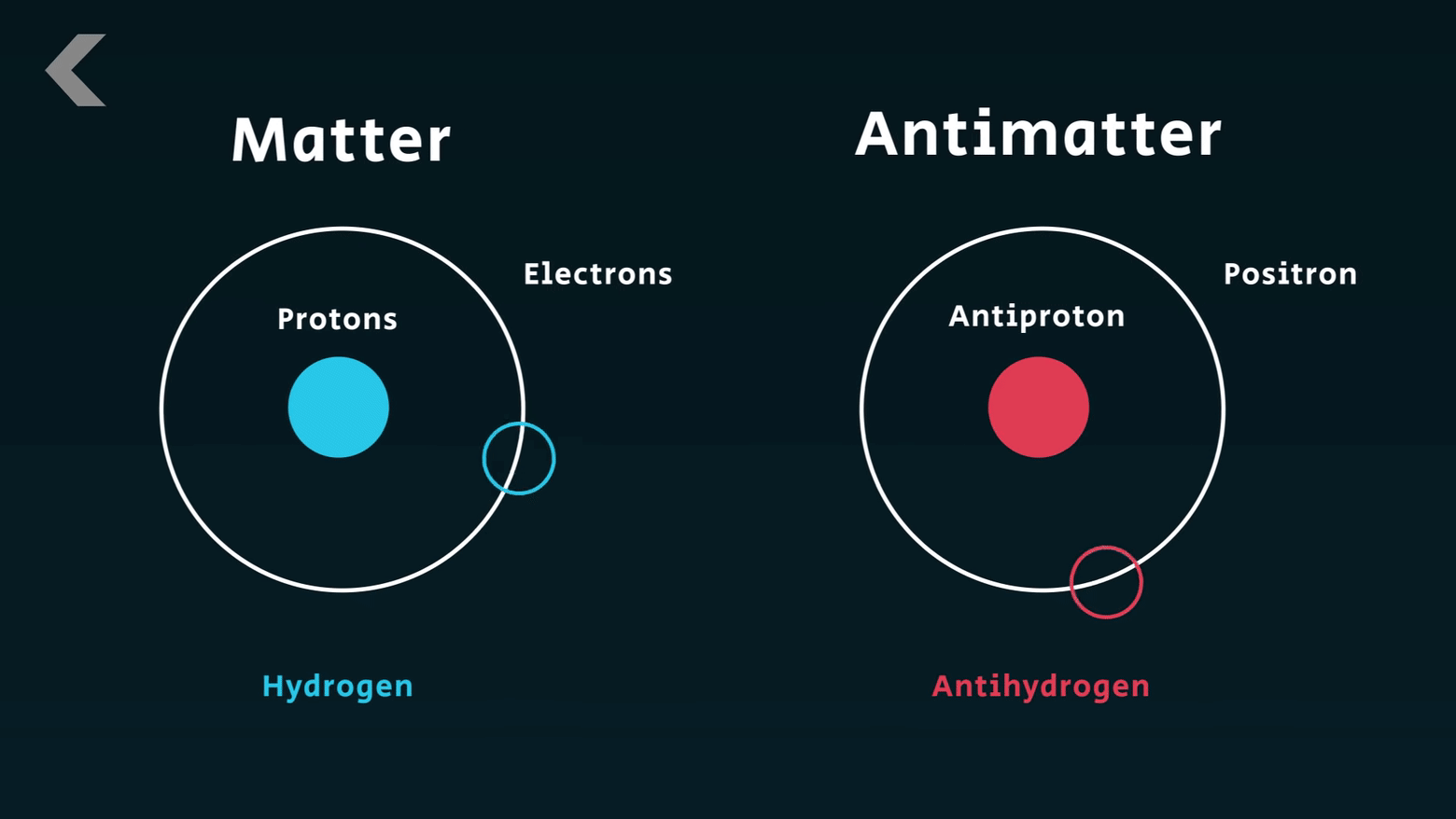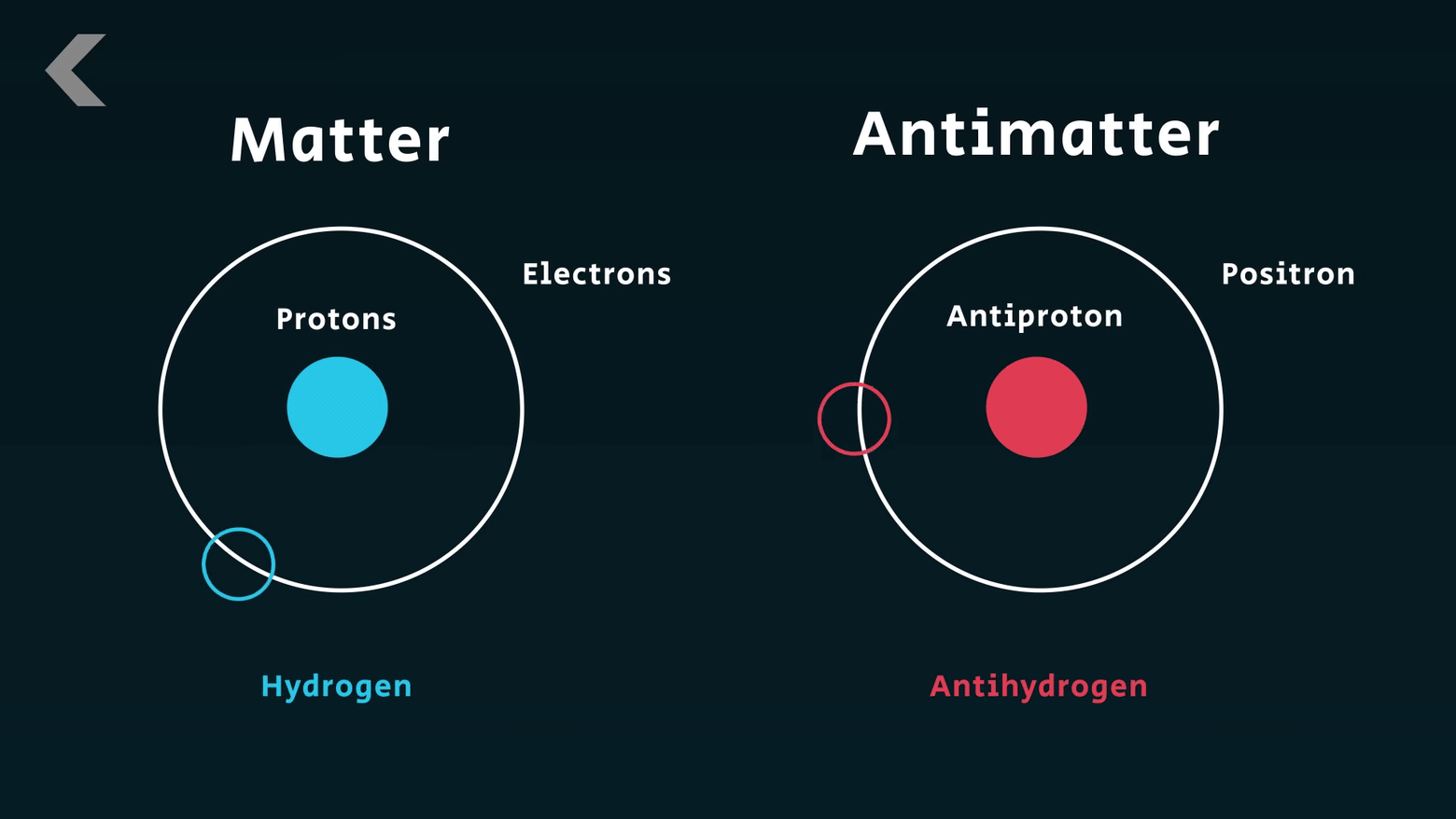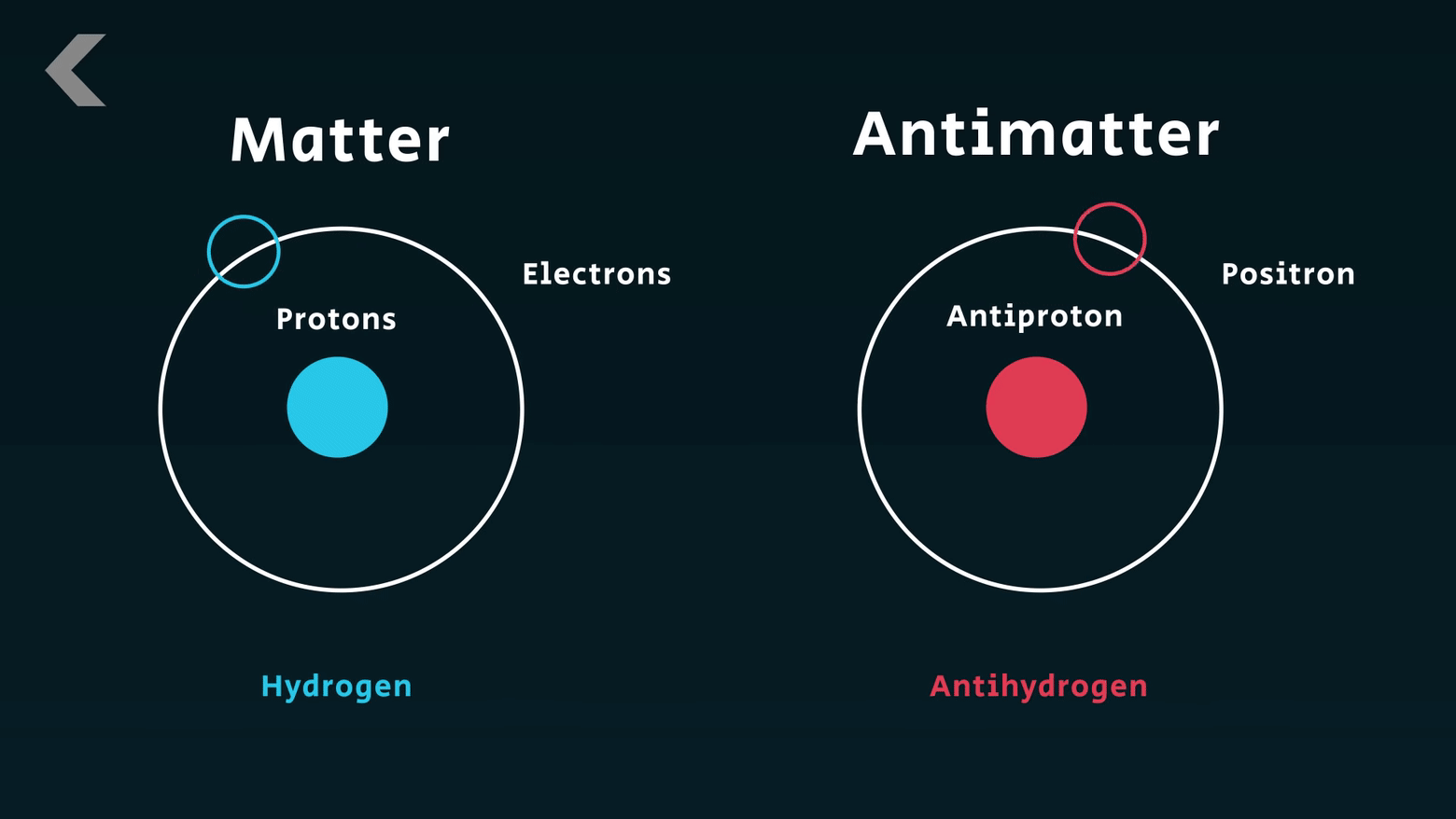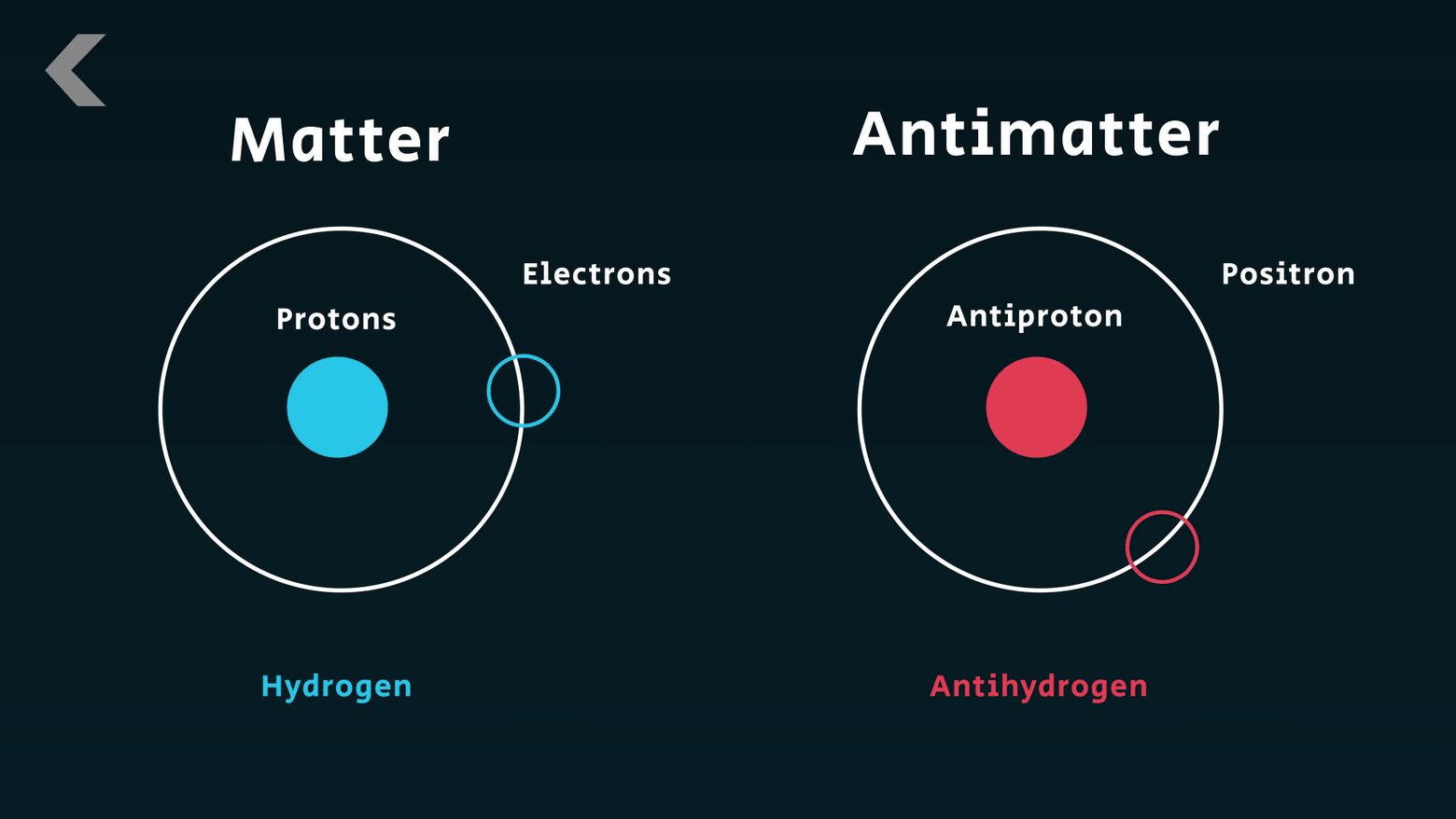
for his discovery of the opposite proton (anti-proton).


Emilio Gino Segre discovered the Anti-proton. Segre passed away on
April 22, 1989, at the age of 84 in the United States. Segre was also active as
a photographer. He also took many photographs documenting events and people in
the history of modern science. They were donated to the American Institute of
Physics after his death. The American Institute of Physics named the photo
archive of the history of physics in its memory.
Source By: Wikipedia.
Information: Dr. P. Ramesh, Assistant Professor of Physics, Nehru Memorial
College, Puthanampatti, Trichy.
Get information like this
https://t.me/joinchat/jpqj3jQLN51kYTk9
Join Telegram Group.
https://chat.whatsapp.com/FisIzCe4Br2CRgxAiicUnf
Join WhatsApp Group
Thanks.
Also, Read
🛑👍 CSIR-NET Physics Materials and Problems
🛑📕 21 GB and Hundreds of Physics E-Books Collection.
🛑🛥️ How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor).
🛑🤹♂️ Science Academies' Summer Research Fellowship Programme for Students and Teachers 2022.
🛑🔌 How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering.
🛑🎙️ Transistors Explained - How transistors work.
🛑🔥⚡ How Thermocouples Work - basic working principle.
🛑🔌 Voltage Explained - What is Voltage? Basic electricity potential difference
🛑🔌 What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics.

.png)
.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment