Today (August 21, 1995) is the Memorial Day of Nobel Prize-winning Indian physicist Subramanian Chandrasekhar, who discovered that a small star could explode and form a bright 'supernova'.
Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar was born on October 19, 1910, in Lahore, Punjab, India (now Pakistan) to C. Subramanian Iyer and Sita Lakshmi Amma. His father worked as a government official. Subramanian Chandrasekhar's family moved to Chennai after spending five years in Lahore and two years in Lucknow. He attended the Hindu High School at Tiruvallikeni in Chennai and later pursued his higher education at the State College and obtained his BA in Physics from the same college. It was during this time in 1928 that his uncle Sir C.V. Rama received the Nobel Prize.
In 1928, when Arnold Sommerfeld came to India, he lectured at the State College in Chennai. Chandrasekhar, who had already read his book, met him and learned about the new research that had taken place in physics and paid close attention to reading books about them. As a result, he published his first research paper the following year. A lecture similar to this article was given at the Indian Science Conference in Chennai that year with the admiration of senior scientists, and his research journey began successfully. Also, the following year at the age of 19, while still an undergraduate, two more articles were published. In 1930, with the gift and financial assistance of the Government of India, Chandrasekhar traveled to Cambridge University for further studies.
Professor R. H., continued his research work as a research student under Fowler, earning a doctorate in 1933 from the University of Cambridge. He later became a research professor at Trinity College, where he met Arthur Eddington, a world-renowned astronomer. He was excited to have the opportunity to interact with his favorite researcher. Later, he returned to the UK and continued his research work, publishing numerous research papers on the structure of galaxies, as well as specializing in various areas of his research. Then, in 1937, he was sought by astronomers at the University of Chicago in the United States. He happily traveled to the United States to continue his work, educating students and continuing his research.
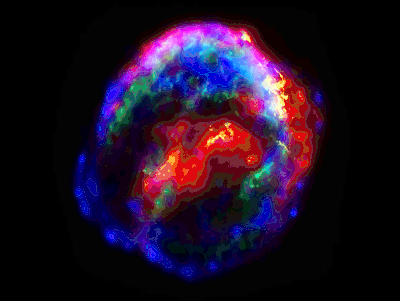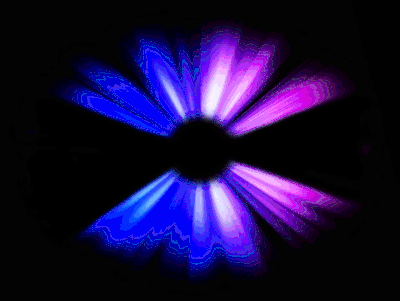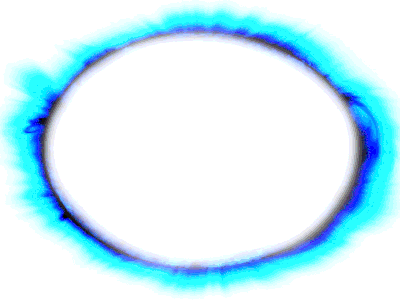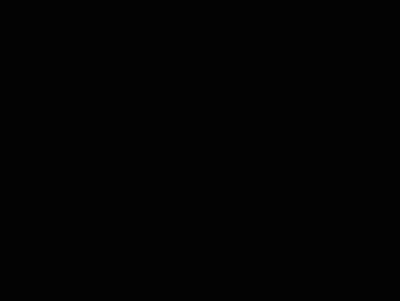
Chandrasekhar was very interested in physics and space science. He excelled in it. He made a definition of the weight of stars in astronomy. The star, which is 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, was found to lose its stability. It is called the Chandrasekhar Limits. He discovered that as the white small star weighed more, its nucleus would explode like a 'nuclear bomb' and form bright 'supernova' stars. He discovered how stars in the Milky Way share the movement of objects. Through this, it was possible to understand the ecosystem of the stars. And discovered why the sky is blue.

In addition to being a well-respected professor at the University of Chicago, he published a book entitled "The Structure of the Stars" which summarizes his research so far. He has also published numerous articles on astronomy, earning him awards and medals from various countries. In 1983, he and William Fowler were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their research on galaxies, taking him to the pinnacle of fame.
While working as an astronomer at the University of Chicago in the United States, he married Lalita, who had studied with him at Presidency College when he came to India. While studying, he was a suitable companion in marriage because they were well acquainted and was the impetus for his research. Subramanian Chandrasekhar, the Nobel Prize-winning Indian physicist, passed away on August 21, 1995, at the age of 84 in Chicago, USA.
Source By: Wikipedia
Information: Dr. P. Ramesh, Assistant Professor of Physics, Nehru Memorial College, Puthanampatti, Trichy.
https://t.me/joinchat/jpqj3jQLN51kYTk9
Join Telegram Group.
https://chat.whatsapp.com/HHC5m0Jz3Ue1E8ilgta0YT
Join WhatsApp Group
Thanks.
Get information like this
https://t.me/joinchat/jpqj3jQLN51kYTk9
Join Telegram Group.
https://chat.whatsapp.com/HHC5m0Jz3Ue1E8ilgta0YT
Join WhatsApp Group
Thanks.
Also, Read
🛑👍 CSIR-NET Physics Materials and Problems
🛑📕 21 GB and Hundreds of Physics E-Books Collection.
🛑🛥️ How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor).
🛑🤹♂️ Science Academies' Summer Research Fellowship Programme for Students and Teachers 2022.
🛑🔌 How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering.
🛑🎙️ Transistors Explained - How transistors work.
🛑🔥⚡ How Thermocouples Work - basic working principle.
🛑🔌 Voltage Explained - What is Voltage? Basic electricity potential difference
🛑🔌 What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics.
Also, Read
🛑👍 CSIR-NET Physics Materials and Problems
🛑📕 21 GB and Hundreds of Physics E-Books Collection.
🛑🛥️ How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor).
🛑🤹♂️ Science Academies' Summer Research Fellowship Programme for Students and Teachers 2022.
🛑🔌 How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering.
🛑🎙️ Transistors Explained - How transistors work.
🛑🔥⚡ How Thermocouples Work - basic working principle.
🛑🔌 Voltage Explained - What is Voltage? Basic electricity potential difference
🛑🔌 What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics.






.png)
.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment