Today (January 30, 1991) is the anniversary of John Bardeen, who two-time winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery invention of the transistor and superconductivity (BCS theory).

John Bardeen was born on May 23,
1908, in Madison, Wisconsin. He was the son of Charles Bardeen, the first dean
of the Wisconsin School of Medicine. Bardeen attended University High School in
Madison. He graduated from school in 1923 at the age of 15. He may have
graduated many years ago, but this was postponed because he had taken courses
at another high school and his mother had died. He entered the University of
Wisconsin in 1923. While attending college, he joined the Zeta Psi fraternity. He
chose to engineer because he did not want to be an educator like his father. He
felt that engineering has good job opportunities.

Bardeen earned his Bachelor of
Science degree in electrical engineering in 1928 from the University of
Wisconsin-Madison. He graduated in 1928, despite taking a year's leave to work
in Chicago. He took all the undergraduate courses in Physics and Mathematics.
He graduated in five years instead of the usual four. This is Leo J. This
allowed him time to complete his master's thesis, overseen by Peters. He
graduated from Wisconsin in 1929 with his Master of Science in Electrical
Engineering. Bardeen developed his studies by staying in Wisconsin. But
eventually, he went to work for Gulf Research Laboratories, a research division of
the Pittsburgh-based Gulf Oil Corporation. He studied research in mathematical
physics and earned a doctorate from the University of Pennsylvania.
From 1930 to 1933, Bardin
worked as a geophysicist in developing methods for the interpretation of
magnetic and gravitational observations. After failing to find work in pursuit
of her interest, she was accepted into the graduate program in mathematics at
Princeton University. As a graduate student, Bardeen studied mathematics and
physics. Under physicist Eugene Wigner, he wrote his thesis on a problem in
solid-state physics. Before completing his thesis, he was awarded the Fellows
Society's Junior Fellow at Harvard University in 1935. He spent the next three
years working with the Nobel laureates in physics from 1935 to 1938. John
Hasbrook Van Vleck and Percy Williams Bridgeman did some work on the problems
of synchronization and electrical conductivity in metals, as well as the
density of the nuclei.

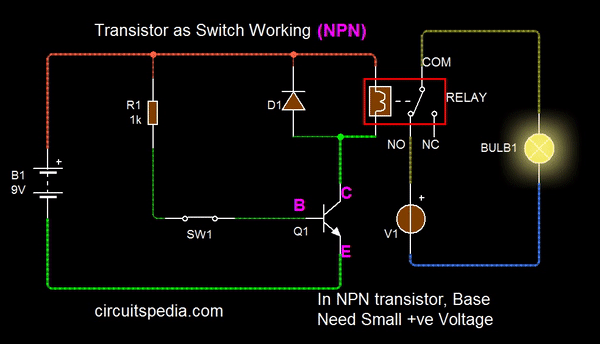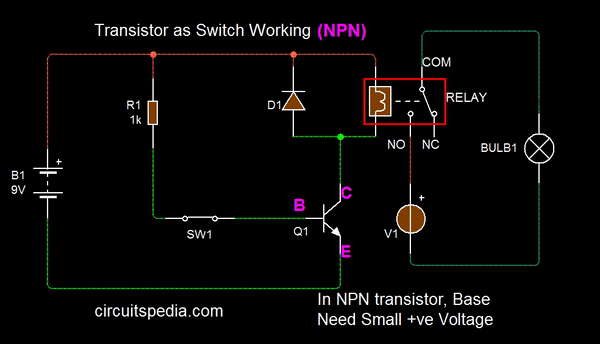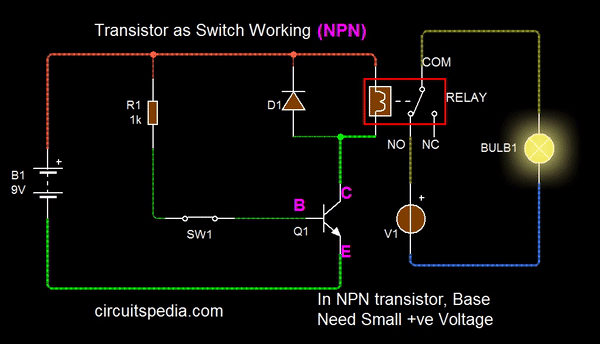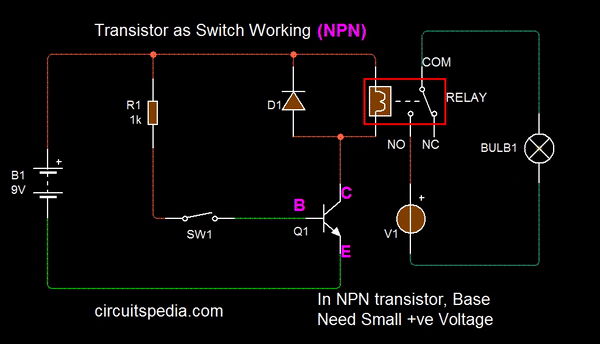
On December 23, 1947, Bardeen and
Bratton worked without Shackley. They succeeded in creating a point-contact
transistor. Within the next month, they began working on Bell Labs' patent
applications. Bell Labs' lawyers soon discovered that Shackley's field-effect
policy was anticipated and patented in 1930 by Julius Lilienfeld, who filed
his Mesfet-like patent in Canada on October 22, 1925. Shockley has publicly
taken on the role of pride for the invention of transistors. This led to the
deterioration of Bardeen's relationship with Shackley. However, Bell Labs management
continued to provide all three inventors as a team. Shockley eventually angered
and alienated Bardeen and Bratton. He also prevented them from working on the
transistor. Bardeen began to pursue a theory of superconductivity. He left Bell
Labs in 1951. Bratton refused to work with Shackley and was appointed to
another committee.

The number of vacuum tubes
transferred to "transistor" televisions and radios is 1/50. It used
very little power, was very reliable, and allowed it to become an electrical device. The transistor is an electronic device called a transistor. It is a semiconductor
device that can be used to amplify the basic electrical signals and switches
that can be used to transmit or transmit electrical signals as needed. Today's
computers, cell phones, and countless electronic control devices are made up of
electrical circuits connected by these networks. He served in the American Sea
War Laboratory during World War II. Bell then worked at the telephone lab.


He was the only person to win the
Nobel Prize for Physics twice. He first won the Nobel Prize twice with William
Shockley and Walter Bratton for their discovery of the tripod in 1956, and in
1972 with Leon Cooper and John Schreiber for refining the theory of
hypersensitivity. Their findings are the basis for later reconstruction
studies. He has extensively investigated the properties of shortcomings. In
1990, John was featured on Bardeen Life's "100 Greatest Americans of the
Century" list. The two-time winner, John Bardeen, left his world on January
30, 1991, at the age of 82 at the Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston,
Massachusetts.
Source By: Wikipedia
Information: Dr. P. Ramesh, Assistant
Professor of Physics, Nehru Memorial College, Puthanampatti, Trichy.
Get information like this
https://t.me/joinchat/jpqj3jQLN51kYTk9
Join Telegram Group.
https://chat.whatsapp.com/FisIzCe4Br2CRgxAiicUnf
Join WhatsApp Group
Thanks.
Also, Read
🛑👍 CSIR-NET Physics Materials and Problems
🛑📕 21 GB and Hundreds of Physics E-Books Collection.
🛑🛥️ How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor).
🛑🤹♂️ Science Academies' Summer Research Fellowship Programme for Students and Teachers 2022.
🛑🔌 How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering.
🛑🎙️ Transistors Explained - How transistors work.
🛑🔥⚡ How Thermocouples Work - basic working principle.
🛑🔌 Voltage Explained - What is Voltage? Basic electricity potential difference
🛑🔌 What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics.
.jpeg)
.png)
.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment