Today (July 15, 1919) is the Memorial Day of Nobel laureate Hermann Emil Louis Fischer, who invented methods of synthesizing sugar and purine block compounds.

Hermann Emil Fischer was born on
October 9, 1852, to Lawrence Fischer, a businessman in Uzbek, near Cologne, and
his wife, Sully Poenzuken. After graduating, his father became involved in
business with his family. This continued until Fischer was deemed unfit for the
field, after which Fischer joined the University of Bonn in 1871. He moved to
the University of Strasbourg in 1872. In 1874 he completed his research on pathology under the guidance of Adolf von Bayer. At the same university, Bayer
was asked to continue his work as a chemist at the University of Munich in
1875. Fischer went with Bayer to assist in his work on organic chemistry.
In 1878 he received the PD-Privatdozent (PD-Privatdozent) at the University of Munich, an accredited qualification for teaching a subject at the university level in German universities. In 1879 he was appointed Associate Professor in the Department of Analytical Chemistry. In the same year, he was invited to serve as Head of the Department of Chemistry at the University of Afghanistan. But Fischer denied it. In 1881 he was appointed Professor of Chemistry at the University of Erlangen. In 1883 Bedice was asked to lead his scientific laboratory by aniline-und soda fabric. However, Fischer's father gave priority to academic work as he had done enough to manage his economy independently and independently.
In 1885 he was invited to become a professor of chemistry at the University of Ursburg. Here he remained until
1892. Then A.W. at the University of Berlin. Fischer was asked to be head of
the chemistry department following Opman. In 1875, while working with von Bayer
at the University of Stasberg,
Fischer discovered phenylephrine hydrogen. This compound has played an
important role in later studies of fissure sugars. While at the University of
Munich, Fischer continued his research on hydrogen with his brother-in-law,
Otto Fischer. Fischer and Otto co-authored a new theory of triphenylmethane
dyes and demonstrated it experimentally. At the University of Erlangen, Fischer
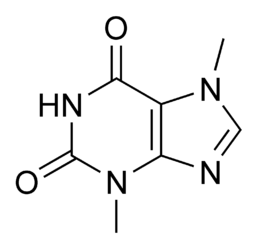
studied the principles behind tea, coffee, chocolate, and cocoa. He studied the
pine and theobromine found in them and established a series of such compounds
and their synthesis methods. However, studies on purines and sugars have
largely contributed to Fischer's popularity.
Studies between 1882 and 1906
revealed that all the little-known compounds at the time, such as adenine,
xanthine, caffeine, and uric acid from animal waste, such as guanine, were
homozygous and could be derived from one another. Furthermore, they
were associated with different hydroxyl and amino derivatives, including the
basic structure of bilayer nitrogen, a characteristic urea group. In 1884 he
first called purine, a hitherto indistinguishable, ideological, supernatural mother.
He also demonstrated purine in 1898 as a compilation. Between 1882 and
1896, several synthetic derivatives that were almost identical to those
found in nature began to emerge from his laboratory.

In 1884 Fischer began his specialized study of sugars. It is possible
that this study changed the knowledge about these compounds and fully
incorporated the new knowledge related to them. As early as the 1880s, the
aldehyde formula of glucose was indicated. However, he established a series of
changes, including the possibility of the formation of phenylephrine hydrogen
and ozone as a result of the reaction of altonic acid, obtained by the
oxidation of fissure sugars, with his discovery of phenyl hydrogen. In 1888 he
established the relationship between glucose, fructose, and monoxide, with a
common ozone-forming reaction. In 1890, he also established the
three-dimensional chemistry and modification of sugars by epimerization between
gluconic acid and mononic acid. Between 1891 and 1894 he established a
three-dimensional system for all sugars known at the time. Furthermore, Vandkop
and Le Bell, published in 1874, used their sharp application of the theoretical
theory of the carbon atom to accurately predict potential modified systems for
sugar.

It is possible that the reverse synthesis methods, which alternate
between different exosols, pentoses, and epochs using processes such as
step-down, compilation methods, and modification, made him realize the value of
the method of compilation methods. His greatest success in 1890 was the
synthesis of glucose, fructose, and monoxide from glycerol. All these special
works on sugars were made between 1884 and 1894. This is followed by a series
of studies on glucosides, which are considered to be the most important
function of fissure.
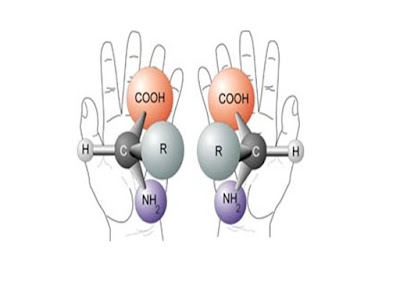
Between 1899 and 1908, Fischer made significant contributions to the knowledge of proteins. In an attempt to find effective analytical methods for identifying and extracting individual amino acids, he discovered new types of ring amino acids such as proline and hydroxyproline. He also studied the synthesis of proteins from amino acids that exhibit optical properties. He discovered the type of binding that causes amino acids in proteins to be chained together. This is what is called peptide binding.
With this start he developed typhobides, tripeptides, and then
polypeptides. In 1901, Ernesto co-founded the glycyrrhizin type of glycine with
Borneo. In the same year he also published the results of his study on the
hydrolysis of the case. Naturally available amino acids were produced in
laboratories and new ones were discovered. His oligopeptide synthesis may have
peaked when octodecopeptide was formed. This octodecapside had many properties
of natural proteins. This study and his subsequent studies may have led to a
better understanding of proteins and additional studies on proteins.
In addition to the tasks already mentioned, he has been studying the enzymes and chemicals found in ficus and elixir, as well as the chemicals used in tanning. He also studied fats in the last days of his life. In 1890, he proposed the concept of a "lock-key model" for observing the interaction between a substrate and an enzyme. Subsequent studies, however, do not support this principle in the reactions of enzymes. When he went to the University of Berlin he realized that he was a staunch fighter in administrative work related to scientific foundations and all fields of study, not just chemistry. His deep understanding of scientific problems, his intuition, his interest in discovering the truth, and his fascination with the pursuit of experimental proof for hypotheses, propose him as the greatest scientist of all time.

He was awarded the 1902 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his discovery of
methods for synthesizing sugar and purine block compounds. He discovered the
Fischer esterification reaction. He developed a pre-range model that could be
used to draw amorphous carbon atoms and indicate their structure. This is
called the Fischer projection model by his name. Hermann Emil Louis Fischer
committed suicide in Germany on July 15, 1919, at the age of 66, due to the
pain of cancer caused by the effects of phenylephrine.
Source: Wikipedia
Information: Dr. P. Ramesh, Assistant Professor of Physics, Nehru Memorial
College, Puthanampatti, Trichy.
Get information like this
https://t.me/joinchat/jpqj3jQLN51kYTk9
https://chat.whatsapp.com/HHC5m0Jz3Ue1E8ilgta0YT
Thanks.
Get information like this
https://t.me/joinchat/jpqj3jQLN51kYTk9
Join Telegram Group.
https://chat.whatsapp.com/HHC5m0Jz3Ue1E8ilgta0YT
Join WhatsApp Group
Thanks.
Also, Read
🛑👍 CSIR-NET Physics Materials and Problems
🛑📕 21 GB and Hundreds of Physics E-Books Collection.
🛑🛥️ How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor).
🛑🤹♂️ Science Academies' Summer Research Fellowship Programme for Students and Teachers 2022.
🛑🔌 How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering.
🛑🎙️ Transistors Explained - How transistors work.
🛑🔥⚡ How Thermocouples Work - basic working principle.
🛑🔌 Voltage Explained - What is Voltage? Basic electricity potential difference
🛑🔌 What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics.
Also, Read
🛑👍 CSIR-NET Physics Materials and Problems
🛑📕 21 GB and Hundreds of Physics E-Books Collection.
🛑🛥️ How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor).
🛑🤹♂️ Science Academies' Summer Research Fellowship Programme for Students and Teachers 2022.
🛑🔌 How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering.
🛑🎙️ Transistors Explained - How transistors work.
🛑🔥⚡ How Thermocouples Work - basic working principle.
🛑🔌 Voltage Explained - What is Voltage? Basic electricity potential difference
🛑🔌 What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics.
.jpeg)
.png)
.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment